
A comprehensive head-to-toe assessment is done on patient admission, at the beginning of each shift, and when it is determined to be necessary by the patient’s hemodynamic status and the context. The head-to-toe assessment includes all the body systems, and the findings will inform the health care professional on the patient’s overall condition. Any unusual findings should be followed up with a focused assessment specific to the affected body system.
A physical examination involves collecting objective data using the techniques of inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation as appropriate (Wilson & Giddens, 2013). Checklist 17 outlines the steps to take.
2. Skin, hair, and nails:
Redness of the skin at pressure areas such as heels, elbows, buttocks, and hips indicates the need to reassess patient’s need for position changes.
Unilateral edema may indicate a local or peripheral cause, whereas bilateral-pitting edema usually indicates cardiac or kidney failure.
Slow pupillary reaction to light or unequal reactions bilaterally may indicate neurological impairment.

Dry mucous membranes indicate decreased hydration.
Use of accessory muscles may indicate acute airway obstruction or massive atelectasis.
Jugular distension of more than 3 cm above the sternal angle while the patient is at 45º may indicate cardiac failure.
The presence of crackles or wheezing must be further assessed, documented, and reported. Unusual findings should be followed up with a focused respiratory assessment.
 Auscultate anterior chest. Blue dots indicate stethoscope placement for auscultation" width="300" height="199" />
Auscultate anterior chest. Blue dots indicate stethoscope placement for auscultation" width="300" height="199" /> 

Hyperactive bowel sounds may indicate bowel obstruction, gastroenteritis, or subsiding paralytic ileum.
Hypoactive or absent bowel sounds may be present after abdominal surgery, or with peritonitis or paralytic ileus.
Pain and tenderness may indicate underlying inflammatory conditions such as peritonitis.
Unusual findings in urine output may indicate compromised urinary function. Follow up with a focused gastrointestinal and genitourinary assessment.
Unusual findings with bowel movements should be followed up with a focused gastrointestinal and genitourinary assessment.

Palpate pulses for symmetry in rate and rhythm. Asymmetry may indicate cardiovascular conditions or post-surgical complications.
Unequal handgrip and/or foot strength may indicate underlying conditions, injury, or post-surgical complications.
CWMS: colour, warmth, movement, and sensation of the hands and feet should be checked and compared to determine adequacy of perfusion.
Check skin integrity and pressure areas, and ensure follow-up and in-depth assessment of patient mobility and need for regular changes in position.
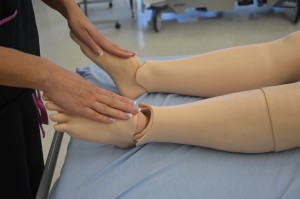
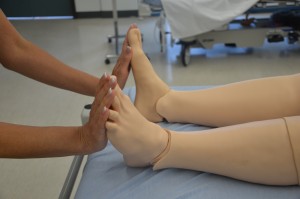


Palpate and inspect capillary refill and report if more than 3 seconds.


To check capillary refill, depress the nail edge to cause blanching and then release. Colour should return to the nail instantly or in less than 3 seconds. If it takes longer, this suggests decreased peripheral perfusion and may indicate cardiovascular or respiratory dysfunction. Unusual findings should be followed up with a focused cardiovascular assessment.

Critical Thinking Exercises
Clinical Procedures for Safer Patient Care Copyright © 2015 by Glynda Rees Doyle and Jodie Anita McCutcheon is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.